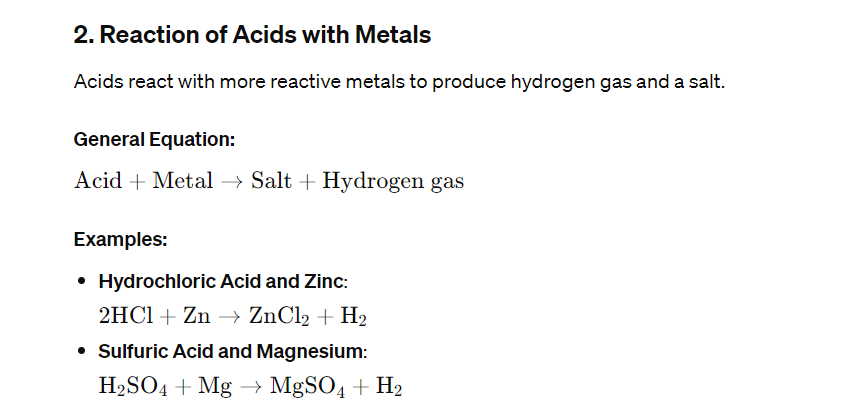Chemical changes are processes where one or more substances are converted into new substances with different physical and chemical properties. These changes are fundamental to chemical reactions and are integral to understanding how substances interact in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Characteristics of Chemical Changes
- Formation of New Substances: The most notable sign of a chemical change is the production of one or more new substances, which may have different properties from the original reactants.
- Irreversibility: Many chemical changes are difficult to reverse, meaning they often require significant energy or another chemical reaction to restore the original substances.
- Energy Changes: Chemical changes are often accompanied by energy changes; energy can be absorbed or released in the form of light, heat, sound, or electrical energy.
- Color Change: A change in color indicates a chemical change (not always exclusive to chemical changes, as some physical changes also involve color changes).
- Gas Production: The formation of a gas (bubbling or odor change) often indicates a chemical reaction, especially if the gas is not a result of boiling.
- Precipitate Formation: The production of a solid from a solution during a chemical reaction signifies a chemical change. This solid is known as a precipitate.
Examples of Chemical Changes
- Rusting of Iron: Iron reacts with oxygen and water to form rust (iron oxides).
- Burning of Wood: Wood combusts in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ash.
- Digestion of Food: Enzymes in the body break down food into simpler molecules that the body can use.
- Photosynthesis: Plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight.
- Cooking an Egg: Heat changes the proteins in the egg from a liquid to a solid.
Evidence of Chemical Changes
To identify a chemical change, look for observable indications such as:
- Change in temperature or heat production.
- Change in color.
- Formation of a precipitate.
- Production of a gas (bubbles or new odor).
Chemical Equations
Chemical changes are represented by chemical equations, which must be balanced to show that mass is conserved in the reaction. A balanced equation has equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.

Importance of Chemical Changes
Understanding chemical changes is crucial for numerous applications:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Production of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other materials.
- Environmental Science: Understanding pollutant transformations and natural biogeochemical cycles.
- Energy Production: Processes like combustion in engines or fuel cells.
- Biological Processes: Metabolic reactions that sustain life.
Conclusion
Chemical changes are an essential aspect of studying science as they provide deep insights into the composition and behavior of matter in various environments and conditions. Recognizing and understanding these changes help in the application of scientific knowledge to solve practical problems, from industrial synthesis to environmental management.